Elements
There are 26 elements in the human body
There are 11 major elements,4 of which (C,H,O,N) make up 96%
There are 15 trace elements that make up less than 2%
Important elements of Human Body
Major elements
Oxygen , Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Calcium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sulphur, Sodium, Chlorine and Magnesium
Trace Elements
Iron, Copper, Zinc, Molybdenum, Iodine and Oxygen
- Necessary for cellular respiration
- Lungs -> Blood -> RBC -> Hb -> Tissue -> Cell -> Mitochondria -> Oxidative phosphorylation - > ATP (Energy)
- Oxygen derived free radicals -> Dangerous
- Treatment - Pneumonia, emphysema, RDS and some heart diseases. decompression sickness, Carbon monoxide poisoning, Gas Gangrene.
Importance of Major elements
Carbon - Component of most organic and inorganic molecules
Hydrogen - component of water and most organic molecules. Necessary for energy
Nitrogen - Component of Amino Acids, Proteins and Nucleic Acids.
Calcium - Components of bones and teeth; triggers muscles contraction.
Phosphorus - Backbone of nucleic acids, Imp for energy transfer.
Potassium - imp for nerve function.
Importance of Trace Elements
Iron - Component of haemoglobin in blood, redox reactions
Copper - Component of Many enzymes
Zinc - Component of some enzymes
Molybdenum - Component of some enzymes
Iodine - component of thyroid hormone.
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that occur in living organisms in order to maintain life.
Catabolism
Hydrolysis reactions
Break down larger food molecules in to the smaller chemicals units
Release energy.
Anabolism
Dehydration synthesis
Build larger and more complex chemical molecules from smaller subunits.
Require energy
Organic Molecules
Most Important major groups of organic substances are:
Carbohydrates
proteins
Lipids
Nucleic Acid, Nucleotides and related molecules
Carbohydrates
All contain C, H, O
Divided into 3 types characterized by the length of their carbon chains.
Monosaccharides (Simple Sugars)
•Simple sugars with short carbon chains
•Six carbon sugar – hexose
•Five carbon sugar – pentose
•Most imp simple sugar – Glucose is primary source of chemical energy)
•Pentose – ribose and deoxy ribose are structural component of RNA and DNA
Disaccheride (Double sugars)
Polysaccharides (Complex Sugars)
•Sucrose , maltose and lactose are disaccharides
•Glycogen is a polymer of glucose – polysaccharide
Proteins
• Structural proteins – form structure of cell. Tissues and organ
• Functional proteins – ex: enzymes
• Proteins are chain like polymers made up of multiple subunits or building blocks called amino acids.
Amino Acids
•OH from the carboxyl group of one amino acid and H from the amino group of another amino acid split off to form water plus a new compound called a peptide.
•Proteins are polypeptides.
Level of proteins structure
Four levels of increasing complexity
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary
- Quartnary
Classification of Proteins According to biological function
Structural V/S Functional
•
- Loses its shape – lose its function
- Sensitive to various environmental factors including high temperature, low or high pH and high ionic strength
- If chemical environment is restored, proteins may be renatured and function normally.
Denaturation
•Proteins can also be broken apart by enzymes, called proteases, that digest the covalent peptide bonds between amino acids that are responsible for the primary structure. This process is called proteolysis and is irreversible. Cells contain proteases that are found in lysosomes, membrane bound organelles inside the cell. When cells are disrupted, lysosomes break and release these proteases, which can damage the other proteins in the cell.
Lipids
All Lipids are hydrophobic
Tryglycerides / Fat
Most abundant lipids
Most concentrated source of energy
2 types of building blocks
Glycerol and fatty acids
Each glycerol unit is joined to three fatty acids.
Types of Fatty Acids
•Saturated and unsaturated
• Saturated – all available bonds of its hydrocarbon chain are filled with hydrogen atoms
• Unsaturated – one or more double bonds in its hydrocarbon chain because not all the chain;s carbon atoms are saturated with hydrogen atoms.
Figure
Saturated – straight, pack closely together and are solid at room temperature
•Unsaturated – more double bonds-more unsaturated. They are liquid at room temperature.
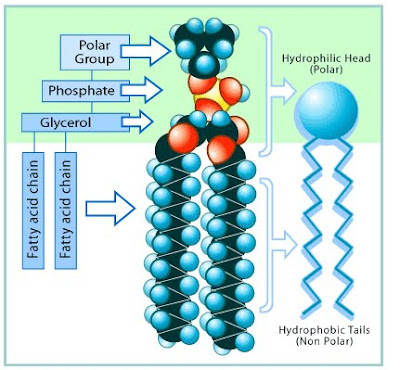
Phospholipids
Similar to triglycerides
One of the three fatty acids attached to glycerol in a triglyceride is replaced by another type of chemical structure cantoning phosphorus and nitrogen.
Figure
•The cell membrane is composed of two layers, each composed of trillions of Phospholipid molecules oriented in a special manner
•The structure that surrounds each of your cells (the plasma or cell membrane) is formed from a Phospholipid bilayer. The polar heads of the phospholipids are all facing the aqueous environments of the outside, and the inside of the cell, while the non-polar tails form a fatty layer on the inside
Steroids
The general structure of cholesterol consists of two six-membered rings side-by-side and sharing one side in common, a third six-membered ring off the top corner of the right ring, and a five-membered ring attached to the right side of that. The central core of this molecule, consisting of four fused rings, is shared by all steroids, including estrogen (estradiol), progesterone, corticosteroids such as cortisol (cortisone), aldosterone, testosterone, and Vitamin D.
Prostaglendins
Also called tissue hormones
•Lipids composed of 20 – carbon unsaturated fatty acids that contain a 5 –carbon ring
Figure
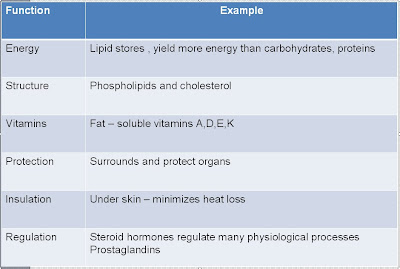
Functions of Lipids
Nucleic Acid
DNA - Adenine and Guanine – purines – double ring structures
Thymine and Cytosine – pyrimidines – single ring structures
RNA - similar except Uracil
DNA
•
RNA
•Mostly single stranded
•Each strand is sequence of ribonucleotides copied from DNA.
Nucleotides - ATP
•Composed of
– Adenosine
• Ribose
• Adenine – nitrogen containing molecule
– Three phosphate subunits
•High energy bonds present between phosphate groups
•Cleavage of bonds release energy
Nucleotides
•NAD & FAD
– Used as coenzymes to transfer energy- carrying molecules from one chemical pathway to another
•cAMP
– Made from ATP by removing two phosphate groups to form a monophosphate
– Used as an intracellular signal
Combined Forms
• Lipoproteins - lipid + proteins
• Glycoproteins – carbohydrates + proteins


















No comments:
Post a Comment